History is not merely the passing of time, nor simply the rise and fall of…
Category: Historical Figures
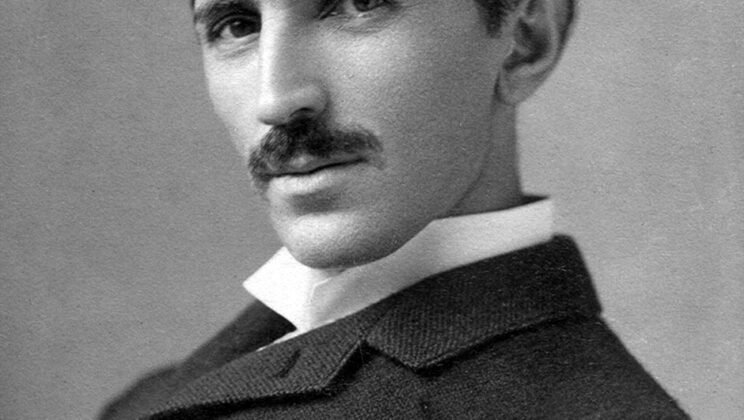
Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla (1856–1943) was a Serbian-American inventor, electrical engineer, and physicist renowned for his groundbreaking…
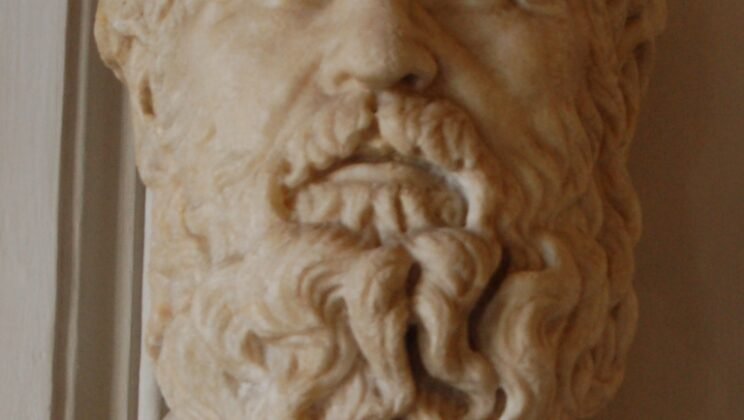
Heraclitus
Heraclitus of Ephesus (c. 535–475 BCE) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher known for his doctrine…
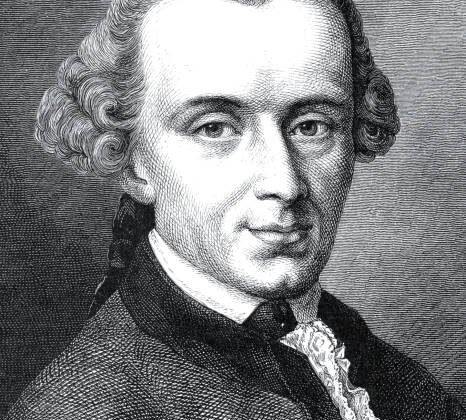
Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant (1724–1804) was a German philosopher whose work significantly shaped modern philosophy and the…
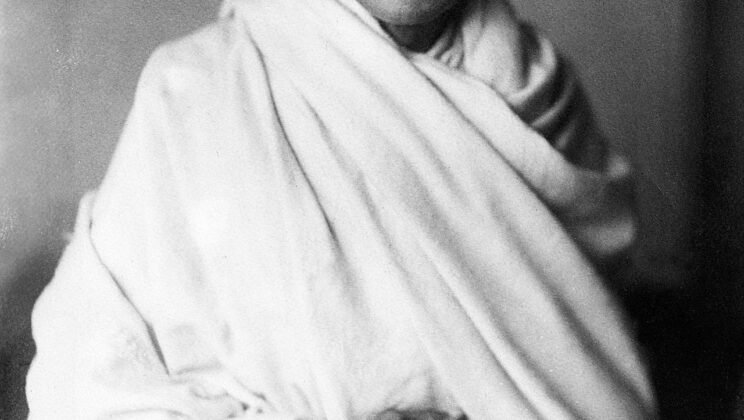
Mahatma Gandhi
Mahatma Gandhi (1869–1948) was a pivotal leader in the Indian struggle for independence from British…
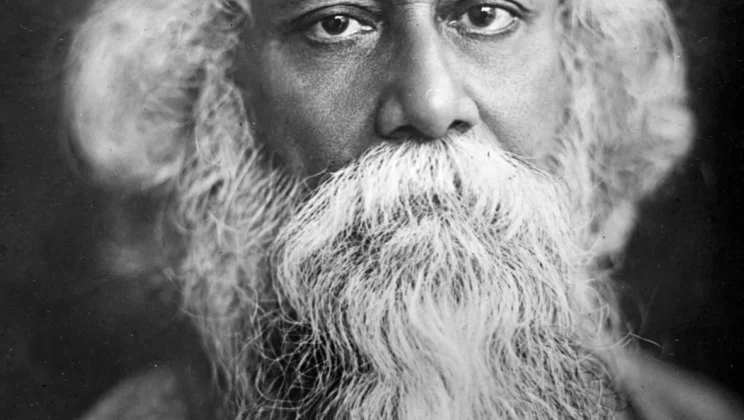
Rabindranath Tagore
Rabindranath Tagore (1861–1941) was an Indian poet, writer, philosopher, and polymath who reshaped Bengali literature…
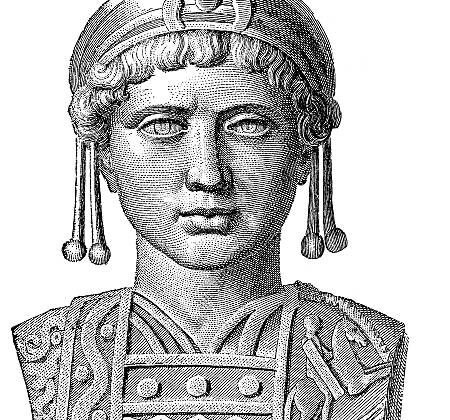
Justinian I
Justinian I (circa 482-565 CE) was Byzantine Emperor from 527 to 565, renowned for his…
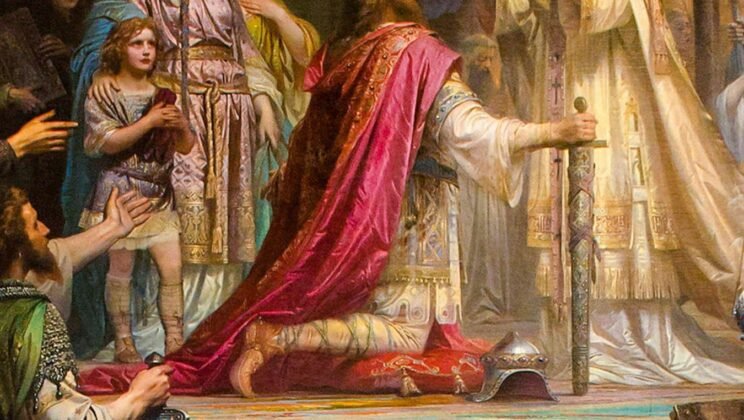
Charlemagne
Charlemagne (circa 742-814 CE), also known as Charles the Great, was King of the Franks…
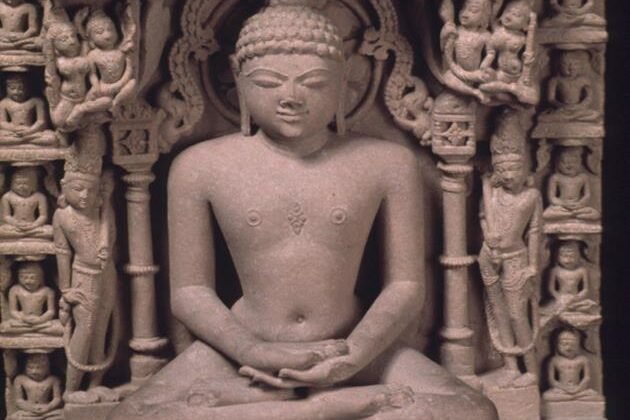
Mahavira
Mahavira (c. 599–527 BCE) was a significant figure in ancient Indian philosophy and the 24th…
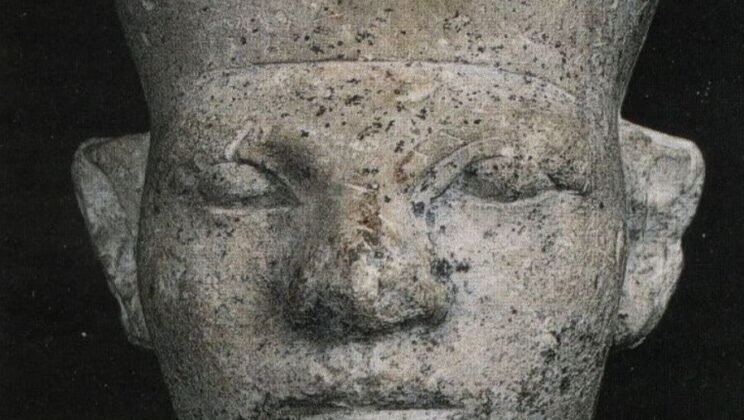
Menes
Menes, also known as Narmer, is traditionally credited with unifying Upper and Lower Egypt around…
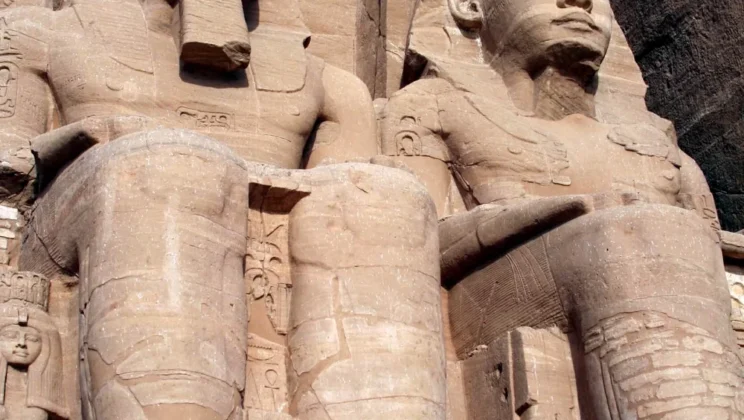
Ramesses II
Ramesses I (c. 1306–1290 BCE) was the founder of Egypt’s 19th Dynasty and played a…
Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (1533–1603) was the Queen of England and Ireland from 1558 until her death…
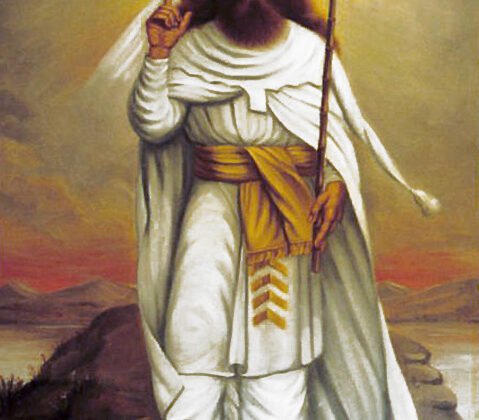
Zoroaster
Zoroaster, also known as Zarathustra, was an ancient Persian prophet and founder of Zoroastrianism, one…
Mencius
Mencius (c. 372–289 BCE) was a Chinese philosopher and a key figure in Confucianism, often…
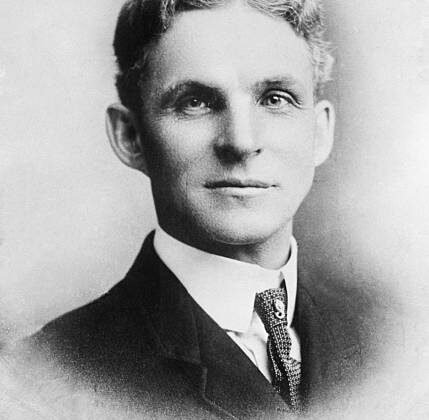
Henry Ford
Henry Ford (1863–1947) was an American industrialist and founder of the Ford Motor Company, renowned…
Francis Bacon
Francis Bacon (1561-1626) was an English philosopher, statesman, scientist, and author who played a key…
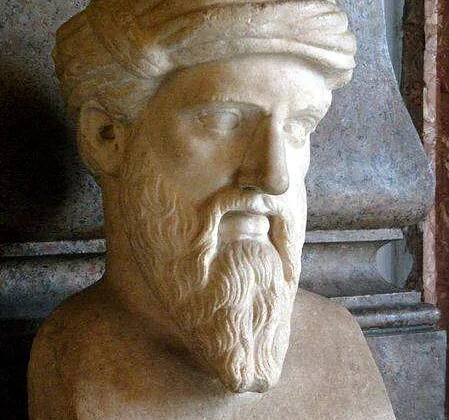
Pythagoras
Pythagoras (circa 570-495 BCE) was an ancient Greek philosopher and mathematician best known for the…
Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong (1893-1976) was a Chinese revolutionary leader and the founding father of the People’s…
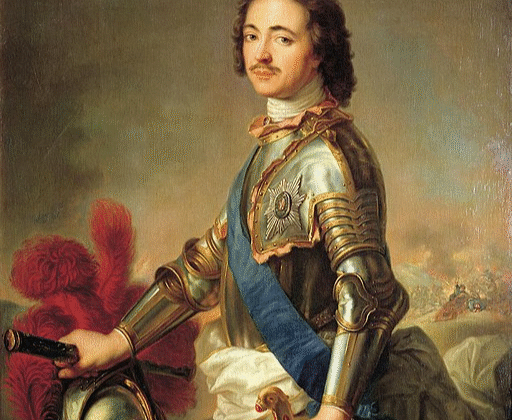
Peter the Great
Peter the Great (1672–1725) was a Russian czar who ruled from 1682 until his death…
Cyrus the Great
Cyrus the Great (c. 600–530 BCE) was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, the first…